A Comprehensive Comparison of Roof Insulation Materials

Exploring the world of roof insulation materials and their comparison, this introduction aims to captivate readers with an informative yet engaging narrative. From an overview of different materials to detailed comparisons, this piece delves into the key aspects that influence the choice of insulation for roofs.
As we navigate through the intricacies of fiberglass, foam board, and spray foam insulation, we uncover the unique characteristics, pros, cons, and installation methods of each material. Let's embark on this journey of discovery together.
Roof Insulation Materials Overview
When it comes to roof insulation materials, there are several options available, each with its own unique characteristics and benefits. Understanding the key features of these materials can help you make an informed decision for your insulation needs.
Fiberglass Insulation
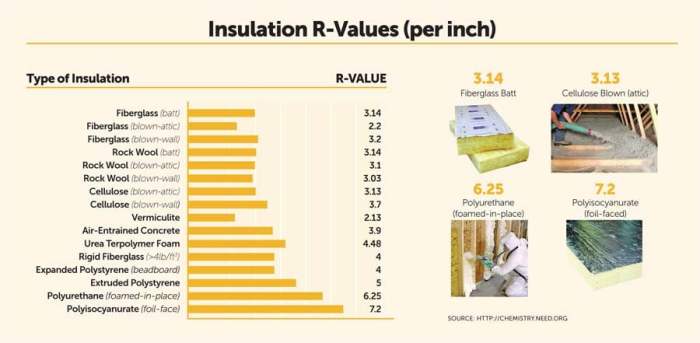
Fiberglass insulation is a popular choice due to its affordability and effectiveness. It is made from tiny glass fibers and is available in batts, rolls, or loose-fill forms. Fiberglass insulation has a moderate R-value per inch, making it a good option for most climates.
- Key Characteristics: Affordable, easy to install, non-flammable
- R-Value: R-2.2 to R-2.7 per inch
- Sustainability: Can be made from recycled materials, but may contain formaldehyde
Spray Foam Insulation
Spray foam insulation is known for its excellent air sealing properties and high R-value. It is applied as a liquid that expands to fill gaps and harden into a solid. While more expensive, spray foam provides superior insulation performance.
- Key Characteristics: Excellent air sealing, high R-value, moisture resistance
- R-Value: R-6 to R-7 per inch
- Sustainability: Can be eco-friendly if made from renewable resources
Cellulose Insulation
Cellulose insulation is made from recycled paper materials treated with fire-retardant chemicals. It is a cost-effective option that provides good thermal performance and sound insulation. Cellulose insulation is typically blown or sprayed into attics.
- Key Characteristics: Made from recycled materials, good sound insulation
- R-Value: R-3.2 to R-3.8 per inch
- Sustainability: Eco-friendly option made from recycled paper
Fiberglass Insulation
Fiberglass insulation is a popular choice for roof insulation due to its affordability and effectiveness in regulating indoor temperature. It is composed of tiny glass fibers that are woven together to create a fluffy material that traps air pockets.
Composition of Fiberglass Insulation
Fiberglass insulation is primarily made of glass fibers that are bound together with a thermosetting resin. This composition allows the material to effectively trap air and prevent heat transfer, making it an excellent insulator for roofs.
Pros and Cons of Using Fiberglass Insulation
- Pros:
- Cost-effective compared to other insulation materials.
- Easy to install, especially in attics and roofs.
- Resistant to mold and mildew growth.
- Cons:
- Can irritate the skin, eyes, and respiratory system during installation.
- May settle over time, reducing its effectiveness.
- Not as effective in blocking air leakage compared to other materials.
Cost-Effectiveness of Fiberglass Insulation
Fiberglass insulation is known for its cost-effectiveness, making it a popular choice for homeowners on a budget. While it may have a lower initial cost compared to other materials, it is important to consider long-term energy savings and insulation effectiveness when making a decision.
Installation of Fiberglass Insulation
Installing fiberglass insulation typically involves laying the material between roof rafters or joists. It is important to wear protective gear, such as gloves, goggles, and a mask, to prevent skin irritation and respiratory issues. Proper installation is crucial to ensure the insulation performs effectively and maximizes energy efficiency.
Foam Board Insulation
Foam board insulation is a type of insulation material made from polystyrene, polyisocyanurate, or polyurethane
Thermal Resistance Comparison
Foam board insulation offers a higher R-value per inch compared to other insulation materials such as fiberglass or cellulose. This means that foam board insulation can provide better thermal resistance with less thickness, making it an efficient choice for insulation projects.
- Foam board insulation typically has an R-value ranging from 4 to 8 per inch, depending on the type of material used.
- In comparison, fiberglass insulation usually has an R-value of around 2.2 to 2.7 per inch, while cellulose insulation ranges from 3.2 to 3.8 per inch.
Moisture Resistance Properties
Foam board insulation is known for its excellent moisture resistance properties. The closed-cell structure of foam board materials prevents water vapor from penetrating the insulation, making it ideal for areas with high humidity levels or potential moisture exposure.
It is important to note that proper installation and sealing of foam board insulation are crucial to maximize its moisture resistance capabilities.
Applications in Different Climates
- In colder climates, foam board insulation is commonly used in exterior walls, roofs, and foundations to provide a barrier against heat loss and moisture infiltration.
- In warmer climates, foam board insulation is beneficial for insulating roofs and walls to reduce heat gain and improve energy efficiency.
- Additionally, foam board insulation can be used in below-grade applications such as basements or crawl spaces to prevent moisture intrusion and maintain thermal comfort.
Spray Foam Insulation
Spray foam insulation is a popular choice for homeowners looking to improve the energy efficiency of their homes. It is a type of insulation that is sprayed into place, where it expands to fill gaps and cracks, creating a tight seal.
Application Process of Spray Foam Insulation
When applying spray foam insulation, professionals use specialized equipment to spray the foam onto surfaces. The foam then expands to fill the space and hardens, creating a seamless barrier against air infiltration.
Air Sealing Capabilities of Spray Foam Insulation
- Spray foam insulation has superior air sealing capabilities compared to other insulation materials.
- It can effectively seal off all gaps and cracks, preventing air leakage and reducing energy loss.
- This tight seal helps to maintain a consistent indoor temperature and improve overall energy efficiency.
Energy Efficiency Benefits of Using Spray Foam Insulation
- Spray foam insulation can significantly reduce heating and cooling costs by preventing air leaks and improving insulation performance.
- It helps to create a more comfortable indoor environment by maintaining a consistent temperature throughout the home.
- The energy savings achieved with spray foam insulation can lead to a decrease in utility bills over time.
Potential Challenges or Drawbacks of Spray Foam Insulation
- One potential drawback of spray foam insulation is its cost, as it tends to be more expensive than other insulation materials.
- Improper installation of spray foam insulation can lead to issues such as off-gassing or poor indoor air quality.
- It is important to hire experienced professionals for the installation of spray foam insulation to ensure proper application and avoid any potential problems.
Ending Remarks

In conclusion, the discussion on roof insulation materials comparison sheds light on the diverse options available for homeowners. Whether prioritizing cost-effectiveness, energy efficiency, or sustainability, there's a suitable insulation material for every need. Make an informed decision for your roof insulation needs and enjoy a more comfortable and efficient living space.
FAQ Guide
What are the key characteristics to consider when comparing roof insulation materials?
Key characteristics to consider include thermal resistance, moisture resistance, installation ease, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability.
Is fiberglass insulation more cost-effective compared to foam board insulation?
Fiberglass insulation is generally more cost-effective upfront than foam board insulation, but long-term costs may vary based on factors like energy savings.
What are the potential challenges of using spray foam insulation?
Challenges of spray foam insulation can include installation complexity, off-gassing odors during application, and the need for professional installation.

